A New Era of Plastic Welding: DVS 2207 Standard and the Path to Future Industrial Upgrades
- Share
- Issue Time
- Mar 18,2025
Summary
Weissenberg explores the DVS 2207 standard and how precise control of temperature, pressure, and heating time improves plastic welding quality. Covering PE, PP, PVC, and PVDF, the article shows real-world results with Weissenberg’s smart welding machines. Learn how PID control and PLC automation boost consistency, efficiency, and performance in industries like chemicals, construction, and new energy.
In modern industrial fields, plastic materials are widely used in industries such as chemicals, construction, medical, and energy due to their excellent processability, corrosion resistance, and cost advantages. As the key process for joining these materials, plastic welding directly determines the service life and safety of products such as pipes, containers, and structural components.
This article will explore the DVS 2207 Standard — the core technical specification in the plastic welding industry — and how precise control of temperature, pressure, and heating time can enhance welding quality. At the same time, we will showcase the real-world application of Weissenberg equipment, demonstrating how to optimize welding processes in production environments to improve both quality and efficiency.
1. DVS 2207: The "Gold Standard" of Plastic Welding
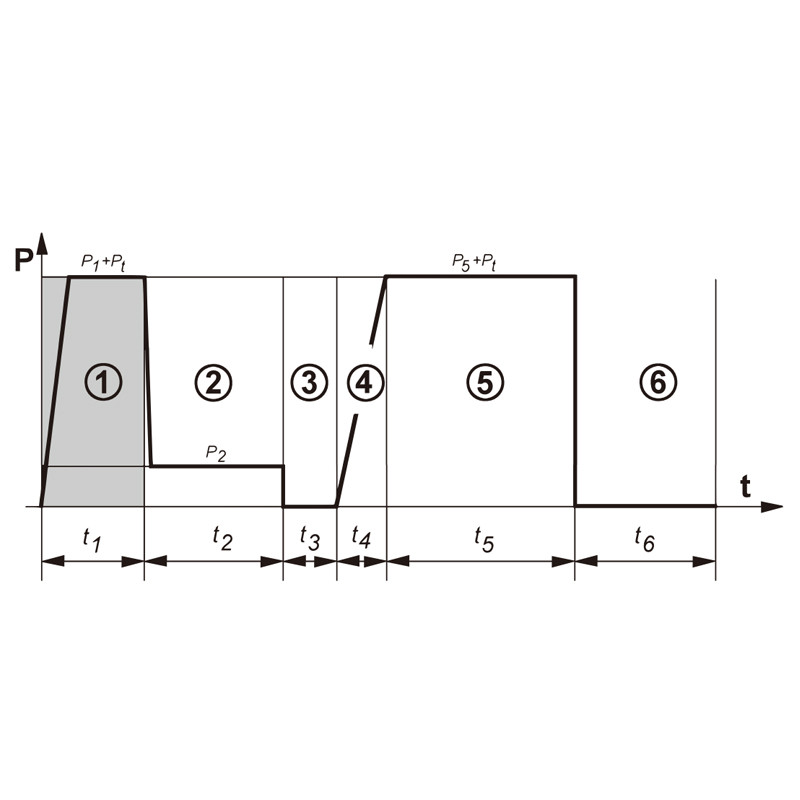
DVS 2207 is an international standard formulated by the German Welding Society (DVS) specifically for guiding the welding of thermoplastic plastics (such as PE, PP, PVC-U, PVC-C, and PVDF). Its core principles are based on precise control of temperature, pressure, and heating time to ensure the strength and durability of welds.
Key Parameters Explained:
| Material Type | Welding Temperature Range (°C) | Welding Pressure (N/mm²) | Heating Plate Temperature Tolerance (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PE (Polyethylene) | 200-220 | 0.01-0.15 | ≤ ±7 |
| PP (Polypropylene) | 200-220 | 0.01-0.1 | ≤ ±10 |
| PVC-U (Rigid PVC) | 222-238 | 0.1-0.6 | ≤ ±8 |
| PVC-C (Chlorinated PVC) | 220-230 | 0.1-0.5 | ≤ ±4 |
| PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) | 232-248 | 0.01-0.1 | ≤ ±8 |
Why Are These Parameters So Important?
- Temperature Control: Too high may cause material degradation, and too low may result in insufficient fusion.
- Pressure Matching: Different materials have different melt viscosities, and pressure must be matched to the material flow characteristics.
- Tolerance Precision: Variations in heating plate temperature affect weld uniformity, and the strict tolerance requirements in DVS 2207 (e.g., ±4°C for PVC-C) help minimize welding defects.
2. Material Application Map: From Lab to Industrial Site
The materials covered by DVS 2207 play key roles in multiple industries:
- PE (Polyethylene)
- Chemical Industry: Corrosion-resistant pipes, tank liners
- Gas/Water Supply: High-pressure transport pipes, make up over 60% of the global plastic piping market
- Medical Field: Disposable protective clothing, sterile packaging[caption id="attachment_19953" align="aligncenter" width="1440"]
 Butt fusion machine[/caption]
Butt fusion machine[/caption]
- PP (Polypropylene)
- Environmental Industry: Wastewater treatment equipment components, such as PP spray towers
- Automotive Industry: Lightweight interiors, battery pack housings
- Food Packaging: Microwave-safe containers[caption id="attachment_19952" align="aligncenter" width="1045"]
 PP spray tower[/caption]
PP spray tower[/caption]
- PVC Series (PVC-U/PVC-C)
- Construction: Drainage pipes, electrical conduit
- Electronics: Circuit board etching tanks, chemical plating containers, such as plating tanks
 PVC Plating Tank[/caption]
PVC Plating Tank[/caption] - PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride)
- New Energy: Lithium battery separators, fuel cell bipolar plates
- Semiconductors: Wafer cleaning tanks, high-purity chemical transfer pipes[caption id="attachment_19958" align="aligncenter" width="1500"]
 PVDF Pipe[/caption]
PVDF Pipe[/caption]
3. Weissenberg Welding Technology: Fine Control for Improved Stability
Although the DVS 2207 standard provides welding guidance, there are still numerous challenges in real-world applications:
- Temperature Instability in Welding: Traditional manual welding methods struggle to control heating temperatures precisely. Too high can degrade materials, while too low may fail to achieve proper fusion.
- Inaccurate Pressure Control: Pressure fluctuations in welding can affect weld consistency, leading to issues such as cracked PVC pipe welds or compromised PP spray tower seals.
- Consistency in Batch Welding: Different operators' skill levels result in inconsistent welding quality, affecting final product performance.
To address these issues, Weissenberg developed welding equipment that enhances welding stability and consistency through precision control systems:
- PID Precise Temperature Control: Heating plate temperature variations are controlled to within ±5°C, ensuring even heating of materials and reducing defects.[caption id="attachment_19961" align="aligncenter" width="570"]
 Heating Plate[/caption]
Heating Plate[/caption] - Intelligent Pressure Adjustment: Automatically matches the melt viscosity of different materials to avoid weak welds or localized stress concentrations.[caption id="attachment_19959" align="aligncenter" width="570"]
 Pressure plate[/caption]
Pressure plate[/caption] - Batch Welding Consistency: The PLC intelligent control system reduces human intervention, ensuring more stable welding quality.[caption id="attachment_19960" align="aligncenter" width="430"]
 Control Panel[/caption]
Control Panel[/caption]
Real-World Case: A certain environmental equipment manufacturer had previously used manual welding methods for PP spray towers. However, they frequently encountered micro-cracks in welds, leading to customer complaints and increased after-sales issues. Since switching to Weissenberg welding equipment, the intelligent temperature control and automatic pressure matching have resulted in a 12% increase in weld strength and a significant improvement in welding consistency. The rework rate was reduced to below 5%.
4. Future Trends: Smart and Sustainable Welding
With the advancement of Industry 4.0, plastic welding is evolving towards smarter and more sustainable practices:
- Data-Driven Welding: By collecting welding process data (such as temperature curves and pressure waveforms) and using AI algorithms, the lifespan of welds can be predicted, and quality traceability can be improved.
- Green Low-Energy Welding: Low-energy heating technologies (such as electromagnetic induction heating) are being adopted to reduce carbon emissions. Weissenberg’s latest equipment integrates energy monitoring systems, saving around 8,000 kWh of electricity annually per unit.
Conclusion: Building on Standards, Breaking Through with Technology
The DVS 2207 Standard serves as the foundation for the plastic welding industry, and continuous optimization of welding equipment takes the industry from "acceptable" to "excellent." Whether used in chemical equipment, environmental devices, or new energy applications, precise welding remains the key to ensuring product performance.
If you're looking for ways to improve welding efficiency and quality, Weissenberg's welding equipment might provide you with a more reliable solution.